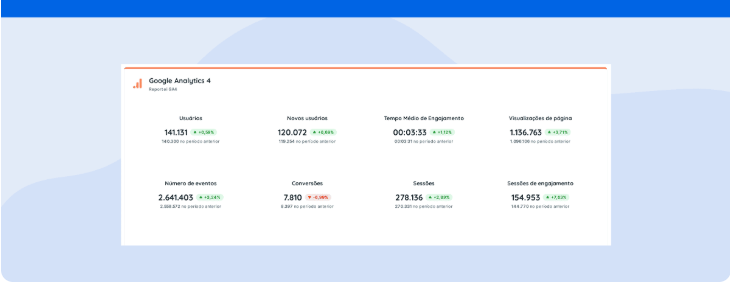
Here’s How Google Analytics tracks direct traffic and how to analyze this metric in your reports
Google Analytics is a true magnet for marketers and customers alike. With its wealth of data, there’s one metric that captures our attention—the mysterious direct traffic.
Understanding where your website visitors come from is crucial. It could mean they typed your URL directly into their browsers or that Google Analytics couldn’t identify the specific channel responsible for the session. But decoding direct traffic goes beyond surface-level knowledge. It requires analyzing it alongside advertising metrics, SEO, social media networks, and more.
To help you navigate this complex realm, we’ve put together an all-encompassing guide that delves into the meaning of direct traffic, how it’s tracked, and what it signifies in your reports. Let’s dive in!
How does GA identify traffic sources?
Before we take a deep dive, let’s shed some light on how Google Analytics (GA) captures this precious information. GA employs several techniques to pinpoint the sources of your traffic. Here are a few notable ones:
- 1. UTM Parameters: By inserting UTM parameters like utm_source, utm_medium, and utm_campaign into your campaigns, GA can accurately trace the origin of your traffic.
- 2. Pixel Tags: Embedding pixel tags in your ads allows GA to track website visits from paid media. These tags help identify user clicks on links that lead to your website.
- 3. HTTP References: GA uses references from landing pages to show where the traffic came from.
- 4. Target Domains: GA leverages the concept of target domains to identify sites that act as referral sources for your site.
- 5. Social Networks: Popular platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn utilize their APIs to enable GA to track visits from shared links across these social channels.
- 6. Direct Traffic: In cases where visitors manually enter the URL into their browsers or the referral source remains unknown or is difficult to identify accurately, GA categorizes it as direct traffic.
Now, when it comes to GA4, capturing data follows a similar pattern. However, GA4 uses event-based tracking instead of the traditional session-based model used by its predecessor, AU.
It relies on the “source” property within events to unveil the traffic source. This property contains crucial information about the website, application, or advertising platform that generates each event.
Moreover, GA4 offers a broader scope of the user lifecycle, enabling comprehensive tracking of user journeys across various platforms and devices. This enhanced understanding of user behavior and traffic sources helps marketers gain valuable insights.
What is direct traffic?
As we discussed earlier, direct traffic encompasses a wide array of website visitors who arrive directly on your pages. They could have entered your URL manually, clicked on their bookmarked links, or come from sources that elude the tracking capabilities of Google Analytics.
Unraveling the true origins of this direct traffic is crucial. It requires a meticulous examination of the potential sources that drive these visits to your website, understanding how they are accounted for within the Google Analytics platform, and deciphering the insights they provide about your digital footprint. Let’s dive right in!
When is direct traffic counted in Google Analytics
Direct traffic in GA can occur in various ways, extending beyond the act of directly typing the URL into the browser. Here are some other things to consider:
- – Accessing bookmarked pages: When visitors access pages saved in their favorites tab.
- – Clicking on untracked mobile app links: Clicking on links within mobile applications that lack UTMs to identify the source.
- – Accessing links in PDFs and e-books: When users click on links within PDFs and e-books.
- – Transitioning from secure to non-secure pages: Moving from a secure (HTTPS) page to a non-secure (HTTP) page.
- – Emails without tracking parameters: Visits originating from emails that lack tracking parameters.
- – Visitors from browsers that block referral information: Visits from browsers that block the transmission of referral information.
- – GA configuration errors: Mistakes in GA setup. For instance, if a page doesn’t have the tool’s tag correctly installed, tracking may be lost when transitioning from that page to another, resulting in the access being labeled as direct traffic.
Just from this list, we can see that direct traffic can be recorded in various ways. That’s why it’s crucial to approach its analysis in reports with caution. By doing so, we can avoid potential errors and ensure a more accurate information-gathering process for our clients.
Analyzing the data in the reports
When delving into the analysis of direct traffic, it’s natural to embark on a focused journey that leads us to the realm of brand recognition.
You see, when visits originate from actions like typing the URL into the browser or accessing bookmarked links, it signifies that users have already encountered the brand through various channels—offline campaigns, word-of-mouth recommendations, or other sources. It’s a clear indication that they are curious and eager to explore the solutions offered by the brand.
In essence, direct traffic serves as a mirror reflecting the effectiveness of your branding strategies. Its growth can be attributed to the activities carried out across multiple media channels, be it digital or traditional.
However, as we mentioned earlier, determining the precise origin of these visits isn’t always a straightforward task. That’s why evaluating direct access alongside other traffic sources becomes crucial. This holistic approach ensures that you capture them accurately and sheds light on any potential issues that might distort the data.
- – Read more: Google Analytics 4: here are the top 10 key metrics
How to get more accurate direct traffic data
To conduct a proper analysis of direct traffic and guarantee the accuracy of your reports, it’s essential to focus on the following crucial points:
- – Make sure that the URLs used in your campaigns, rich assets, and applications are properly tagged using UTM tools such as the URL – Builder. This practice streamlines the tracking process.
- – Ensure that all pages on your website have an active security certificate (HTTPS).
- – Confirm that Google Analytics has been correctly installed and is effectively collecting data across all pages of your website.
Additionally, stay vigilant and monitor any sudden changes that could impact your traffic patterns. Keep a watchful eye on significant shifts, such as a sharp decline in users arriving from paid media campaigns or a noticeable increase in direct visits.
Let Reportei help you track Google Analytics results
If you’re looking to elevate your website metrics analysis to new heights, we have just the solution for you: Reportei’s Google Analytics Universal and Google Analytics 4 reports.
With our powerful tool, you can effortlessly gather data from both Google Analytics platforms, including valuable insights on traffic sources. Say goodbye to the tedious manual tasks that consume your time and energy. Instead, redirect your focus towards what truly matters: making informed decisions that drive project efficiency.
Unlock a simpler and more efficient way of analyzing your website traffic and supercharge your decision-making process by starting your free 3-day trial!